How high can the highest precision be achieved by different machining processes?
With the rapid development of industry, machine tool machining has become increasingly important in industrial production. The machine tools have gradually evolved into common types such as lathes, milling machines, planers, boring machines, drilling machines, and grinding machines. When it comes to the machining processes of various types of machine tools, the machining accuracy must be mentioned. This is used to describe the fineness of product production, and is usually used to describe the geometric parameters of the machined surface. In simple terms, the machining accuracy is inversely related to the tolerance grade. That is, the machining accuracy is expressed in terms of the tolerance grade, and the lower the grade value, the higher the machine tool machining accuracy. Conversely, the higher the tolerance grade value, the lower the machining accuracy.
The "tolerance grade" is explained in Baidu Encyclopedia as "the level that determines the degree of dimensional accuracy, which is divided into 20 grades according to national standards, from IT01, IT0, IT1 to IT18. The larger the value, the lower the machining accuracy, and the larger the allowable range of dimensional changes (tolerance value), the lower the machining difficulty." According to the above text, IT01 indicates that the machining accuracy of the part is the highest, and IT18 indicates that the machining accuracy grade of the part is the lowest. Generally speaking, factory machinery belongs to IT7 grade, and agricultural machinery belongs to IT8 grade.
Depending on the function of the product components, the required machining accuracy is different, and the machining processes chosen by the engineers will also be different. This is a great test of the machining capabilities of CNC machine tool factories and the professional experience of engineers.
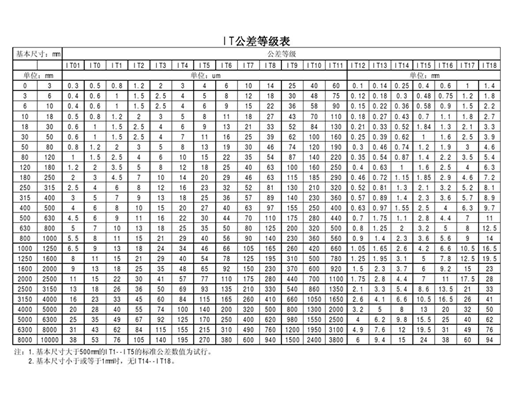
(The IT tolerance grade table is attached)
1. Lathe machining. Generally, turning process is used, that is, the tool moves linearly or in a curved path on a plane to perform cutting. Turning is generally used for the internal and external cylindrical surfaces, end faces, conical surfaces, shaped surfaces, and threads of the workpiece, as well as reverse machining. The turning accuracy is generally IT8-IT7, and the surface roughness is generally 1.6μ~1.8μ.
The editor reminds you that even for lathe machining, there are several classifications, such as rough turning, semi-precision turning, precision turning, and high-precision lathe machining.
Among them:
A. Rough turning. The emphasis is on improving turning efficiency by using a larger depth of cut and feed rate without reducing the cutting speed. However, the machining accuracy of rough turning can only reach IT11, and the surface roughness is Ra20, which is about 10μm.
B. Semi-precision and precision turning. This machining process tries to use high speed and relatively small feed rate and depth of cut. The machining accuracy can generally reach IT10-IT17, and the surface roughness is generally Ra10, which is 0.16μm.
C. High-precision lathe machining. Generally, high-hardness diamond tools are used to machine non-ferrous metal parts, and the machining accuracy can reach IT7-IT5, and the surface roughness is generally Ra0.04, which is 0.01μm. This lathe turning process is called "mirror turning".
2. Milling. Milling refers to the use of a rotating multi-tooth tool to cut the workpiece, which is a highly efficient machining method. It is generally used for machining flat surfaces, grooves, various shaped surfaces (such as splines, gears, and threads), etc. According to the relative direction of the main motion speed and the workpiece feed direction during milling, milling can be divided into up-milling and down-milling.
Milling can be carried out on horizontal milling machines, vertical milling machines, gantry milling machines, tool milling machines, and various special milling machines. For single-piece small-batch production of medium and small parts, horizontal milling machines and vertical milling machines are the most commonly used.
The machining accuracy of milling is generally IT8-IT7, and the surface roughness is generally Ra6.3, which is about 1.6μ.
Among them:
A. The machining accuracy of rough milling is IT11-IT13, and the surface roughness is Ra5, which is 20μm.
B. The machining accuracy of semi-precision milling is IT8-IT11, and the surface roughness is Ra2.5, which is 10μm.
C. The machining accuracy of precision milling is IT16-IT18, and the surface roughness is Ra0.63, which is about 5μm.
3. Planing. This is a cutting machining method in which the planer tool performs a horizontal reciprocating linear motion relative to the workpiece. It is mainly used for the external shape machining of parts. Common planer machines include shaper and planer.
The machining accuracy of planing can generally reach IT9-IT7, and the surface roughness is Ra6.3, which is 1.6μm.
A. The machining accuracy of rough planing can reach IT12-IT11, and the surface roughness is 25, which is 12.5μm.
B. The machining accuracy of semi-precision planing can reach IT10-IT9, and the surface roughness is 6.2, which is 3.2μm.
C. The machining accuracy of precision planing can reach IT8-IT7, and the surface roughness is 3.2, which is 1.6μm.
4. Grinding. Grinding is a machining method that removes excess material from the workpiece using abrasives and grinding tools, and it is a precision machining process widely used in the machinery manufacturing industry. Grinding is usually used for semi-precision and precision machining, and the accuracy can reach IT8-IT5 or even higher. The surface roughness of grinding is Ra1.25, which is 0.16μm.
A. The surface roughness of precision grinding is 0.16-0.04μm.
B. The surface roughness of ultra-precision grinding is 0.04-0.01μm.
C. The surface roughness of mirror grinding can reach below 0.01μm.
5. Drilling. This is a basic way of hole machining. Drilling is usually done on a drilling machine, lathe, boring machine, or milling machine.
The machining accuracy of drilling is generally low, usually only reaching IT10, and the surface roughness is Ra12.5, which is 6.3μm. After drilling, reaming, boring, etc. are usually used as auxiliary operations to complete semi-precision and precision machining.
6. Boring. This is a machining process that uses a tool to perform expansion or other circular profile internal diameter cutting, usually applied between semi-rough machining and precision machining, and the tools used are generally single-edge boring tools or boring bars.
A. The boring accuracy for steel materials can generally reach IT9-IT7, and the surface roughness is 2.5-0.16μm.
B. The machining accuracy of precision boring can reach IT7-IT6, and the surface roughness is 0.63-0.08μm.

